Current State of Global Chip Supply, Power Constraints, & Competition
Dylan Patel, SemiAnalysis | Talal Al Kaissi, Group Chief Global Affairs of G42
Today’s Sourcery is brought to you by Brex..
Brex is the modern finance platform, combining the world’s smartest corporate card with integrated expense management, banking, bill pay, and travel. Over 30,000 companies, including ServiceTitan, Anthropic, Scale AI, Mercor, DoorDash, and Wiz, use Brex to spend smarter and move faster.
As a Sourcery subscriber, you can unlock up to $500 toward Brex travel or $300 in cash back (plus exclusive perks). Start today at brex.com/sourcery
Current State of Global Chip Supply, Power Constraints, & Competition
Last weekend I attended a talk by Dylan Patel of SemiAnalysis on the ‘current state of global chip supply & competition,’ which then inspired me to capture, write, & research a longer form summary of his presentation with a little help from some industry leaders. Break down below!
Special thank you to Dylan Patel Founder of SemiAnalysis, Talal Al Kaissi, Group Chief Global Affairs of G42, Packy McCormick of Not Boring, and Gil Verdon of Extropic, for input, editing, & research.
Chips Chips Chips
The global chip and AI compute ecosystem is undergoing a seismic shift, driven by the explosive growth of large-scale model training and inference. As U.S. demand for GPUs and data center capacity accelerates, countries like the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Saudi Arabia are emerging as both critical partners and potential geopolitical pressure points in the international AI supply chain.
Through landmark GPU deals, these Gulf nations are securing hundreds of thousands of cutting-edge chips annually while investing aggressively in both domestic and U.S.-based data center infrastructure. These agreements represent more than access to semiconductor hardware, they’re signaling a broader realignment of compute capacity, trillions of dollars in capital investment, and energy infrastructure that is foundationally shaping the structure of global AI trade.
It’s becoming increasingly clear: data is the new oil, and compute is the refinery. The immediate real value lies in transforming raw energy into intelligence. Nations that can efficiently convert electricity into tokens, inferences, and cognitive output will hold a major strategic advantage in the emerging trillion-dollar AI economy.
America's Severe Energy Bottleneck & China's Acceleration
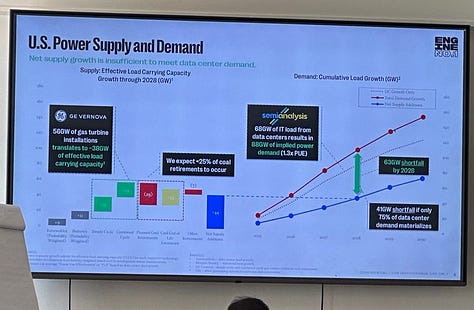
As demand for compute infrastructure skyrockets, the U.S. faces a historic bottleneck, not in talent or chips, but in energy supply. By 2028, AI data centers are expected to drive a total load of 88 GW; domestic grid expansion and permitting delays mean the country will fall 63 GW short. Even under a more conservative scenario where only 75% of projected demand materializes, the U.S. still faces a 41 GW shortfall.
The result is that even companies with the capital to build next-generation data centers—such as Microsoft, Amazon, Meta, Oracle, and OpenAI—are increasingly grid-constrained. In many cases, they have built or leased massive AI campuses but are waiting months or years for full power access.
Causing situations like → xAI is using 35 methane gas generators to power its "Colossus" supercomputer facility
This has led to growing interest in alternative strategies, including:
Colocating data centers near stranded energy (e.g. Crusoe’s flare gas capture).
Investing in private generation & microgrids, especially solar + battery or nuclear small modular reactors (SMRs).
Outsourcing compute abroad to energy-rich nations like the UAE and Saudi Arabia, where projects like Stargate UAE and DataVolt are being deployed rapidly with sovereign support.
Ultimately, the U.S. energy constraint is not just a technical issue—it’s becoming a national competitiveness issue. Without coordinated national efforts to modernize the grid, accelerate permitting, and prioritize AI-relevant energy loads, the U.S. risks being outpaced by rivals with more agile energy infrastructure and sovereign industrial policy.
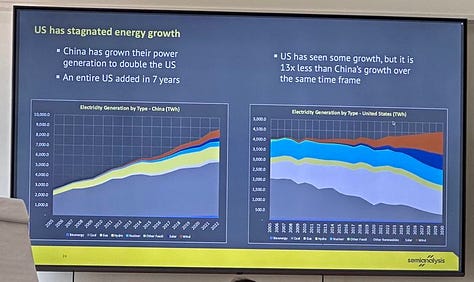
The most dramatic example? China has more than doubled its power generation capacity in just seven years—a pace 13x faster than the U.S.—and is rapidly expanding its domestic chip fabrication capability. With circulating, yet unconfirmed, rumors that China is rolling out a new nuclear reactor every 12 weeks, which may increase to 6 soon. On top of that, if Taiwan’s fabs were disrupted, China could soon surpass the U.S. in advanced wafer capacity, adding to the urgency of reshoring semiconductor production and building allied compute capacity abroad.
Emerging Companies to Watch:
Exowatt: Powering AI with 24-hour Solar. Modular, dispatchable energy systems, built for the demands of AI infrastructure. Exowatt is building domestically to accelerate energy independence and support the industries driving global progress, from AI breakthroughs to critical infrastructure. Exowatt delivers abundant, reliable energy made for the future, made in the USA.
Karman Industries: Developing thermal systems to bring a step function change in energy efficiency across manufacturing, data centers, geothermal, and nuclear.
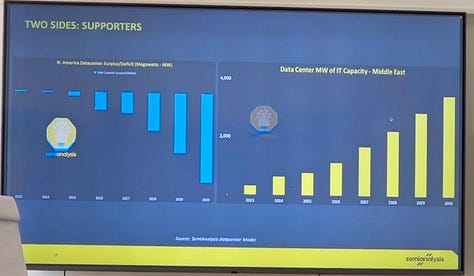
The Gulf’s Infrastructure Bet: G42 & HUMAIN
To bridge this widening infrastructure gap, the U.S. is now partnering with energy-rich Gulf nations that can move fast and deploy massive capital. Nowhere is this more evident than in the recently signed agreement with the UAE’s G42 and the United States. With Saudi Arabia’s HUMAIN is regarded as one of the next most consequential compute initiatives.
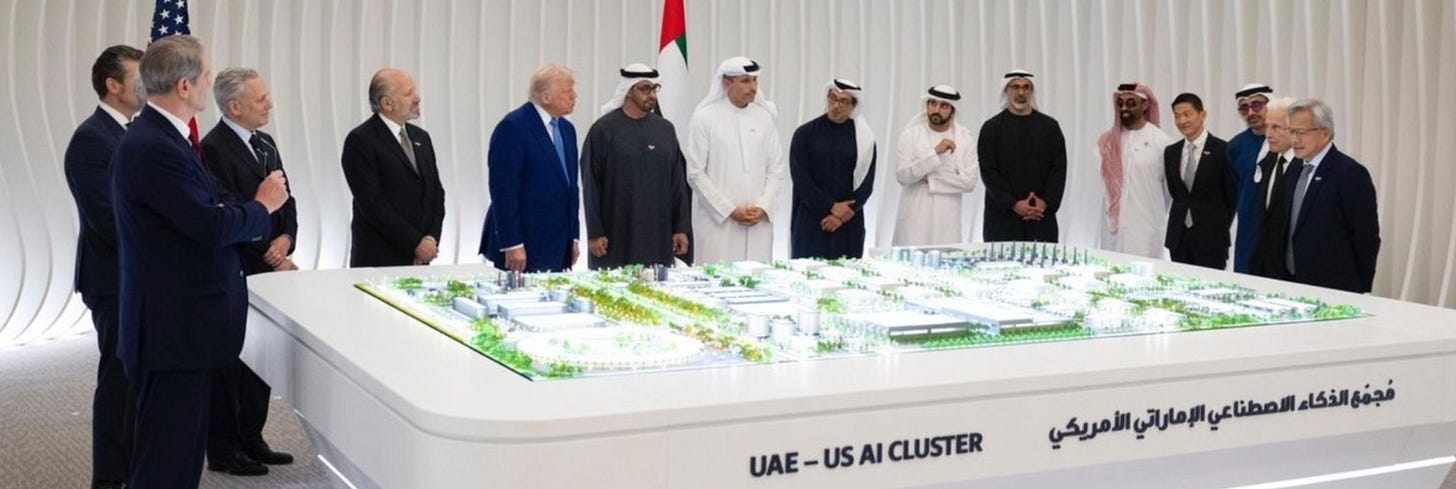
In the UAE, G42 will receive 500,000 GPUs annually, retaining 20% for local deployment for G42 operations and internal workloads. The remaining 80% will be managed by U.S. hyperscalers like Microsoft, OpenAI, and Oracle, both operating under stringent license and audit conditions. This compute is being integrated into a massive buildout: a 5-gigawatt (GW) U.S. UAE AI Campus–already under construction in Abu Dhabi. Of which, Stargate UAE is the 1-gigawatt (GW) anchor, leaving the remaining 4 GW available for hyperscalers and model developers.
"Abu Dhabi’s vision is exactly that: a 5 gigawatt AI campus dedicated to advanced computing. A facility drawing the energy equivalent of 5 nuclear reactors, filled wall-to-wall with cutting-edge AI hardware.” G42
Stargate UAE is the largest AI data center project outside the U.S. and the centerpiece of G42’s broader “Intelligence Grid” strategy: a sovereign, distributed compute backbone that turns electrical energy into AI-generated insight. Powered by NVIDIA’s GB300 NVL72 AI racks, Stargate UAE is projected to output up to 4.3 quadrillion tokens per day, which is more than the total number of words spoken by the entire human race daily.
As Talal Al Kaissi, Group Chief Global Affairs of G42 simply puts it:
Electricity → Computation → Intelligence
“With next-gen platforms achieving ~5× efficiency gains, the token-per-watt yield is rapidly increasing. In a place like the UAE which not only produces cheap solar and nuclear power but also has the ability to deploy thousands of top-tier GPUs, this translates to an intelligence production capacity amplifying countries like the US' ability to manufacture and diffuse intelligence.
A kilowatt-hour that might have fetched a few cents powering an air conditioner can instead generate a thousand clever answers from an AI, or the design for a more efficient solar panel, or a personalized medical insight. It’s a very high-value use of energy. [Arguably the most value-added way to export energy is by first turning it into intelligence!]”
This vision aligns with a decade-old statement by Sheikh Mohamed bin Zayed, now President of the UAE shared in 2015:
“There will be a time, 50 years from now, when we load the last barrel of oil… The question is: after we have loaded this last barrel, are we going to feel sad? If our investment today is right… we will celebrate that moment.”
And that investment has accelerated. In March 2025, following a meeting with President Trump, the UAE pledged a $1.4 trillion commitment to U.S. investments. With capital flowing at that scale, initiatives like Stargate UAE and the broader Intelligence Grid reflect a long-term strategic shift: an industrial pivot from fossil fuel exports to cognitive exports; from barrels of oil to units of intelligence.
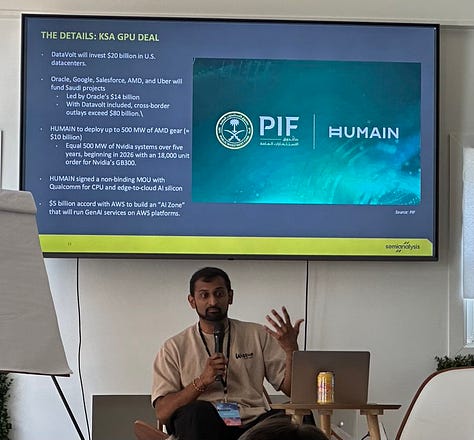
The same logic is being applied in Saudi Arabia. Backed by Oracle, AWS, and the Public Investment Fund (PIF), the HUMAIN initiative is deploying 500 MW each of Nvidia and AMD systems. That buildout is tied to a broader $20 billion investment in U.S. data center infrastructure via DataVolt. HUMAIN is also anchoring projects like the $5B “AI Zone” with AWS and signing MoUs with Qualcomm to build edge-AI infrastructure across the Kingdom.
Companies To Watch:
Groq: Saudi Arabia Announces $1.5 Billion Expansion to Fuel AI-powered Economy with AI Tech Leader Groq
Cerebras: Chipmaker Cerebras Says US Signs Off on UAE Tie Ahead of IPO
Armada: Full-stack edge computing platform. Aramco Digital, Armada, and Microsoft recently collaborated to deploy Armada’s Galleon edge data centers, the Commander software platform, and real-world AI applications in Saudi Arabia.
Read More: UAE and US Presidents attend the unveiling of Phase 1 of new 5GW AI campus in Abu Dhabi
Read more in SemiAnalysis: AI Arrives In The Middle East: US Strikes A Deal with UAE and KSA 5 GW Datacenter, HUMAIN, G42, Diversion and Misuse Risks, Security Requirements, American AI Wins
Risks, Safeguards, & Potential U.S. Leverage
Critics of these deals point to export control risk, arguing that such large-scale GPU shipments may be diverted to China or misused in ways that bypass U.S. oversight. However, supporters note that the deals are structured with multiple layers of governance: auditability, compliance monitoring, KYC for tenants, and hardware isolation between regions. These safeguards are designed to protect U.S. technology while accelerating global access to compute under aligned infrastructure.
Following support by Sriram Krishnan, Senior Policy Advisor for AI at the White House, on the U.S.–Middle East AI partnerships, G42 Executive Talal Al Kaissi shared the "Regulated Technology Environment (RTE)"—a framework the UAE is using to ensure secure collaboration on AI infrastructure. Emphasizing that safeguarding U.S. technologies is not new to G42, pointing to the landmark 2024 Intergovernmental Assurance Agreement (IGAA) between Microsoft and G42. Announced alongside Microsoft’s $1.5 billion investment, the IGAA established a first-of-its-kind security and compliance architecture for cross-border AI deployments. Co-developed with U.S. and UAE government input, the agreement enforces stringent controls around export compliance, national security, AI safety, and model governance.
From the U.S. perspective, these deals offer a lifeline. With permitting bottlenecks, delayed grid upgrades, and fierce competition for power, the Gulf offers a high-speed off-ramp for training and inference workloads. And unlike China, the UAE and Saudi Arabia are deeply intertwined with the U.S. tech stack, reinforcing American platforms across OpenAI, Microsoft Azure, Oracle, and Nvidia. The alternative—ceding that compute territory to Beijing—poses a much greater strategic risk.
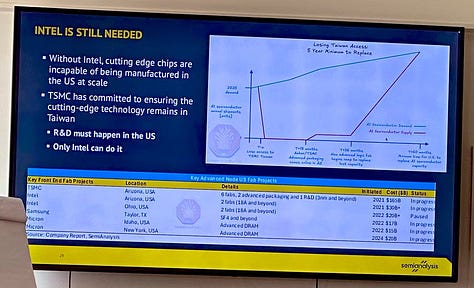
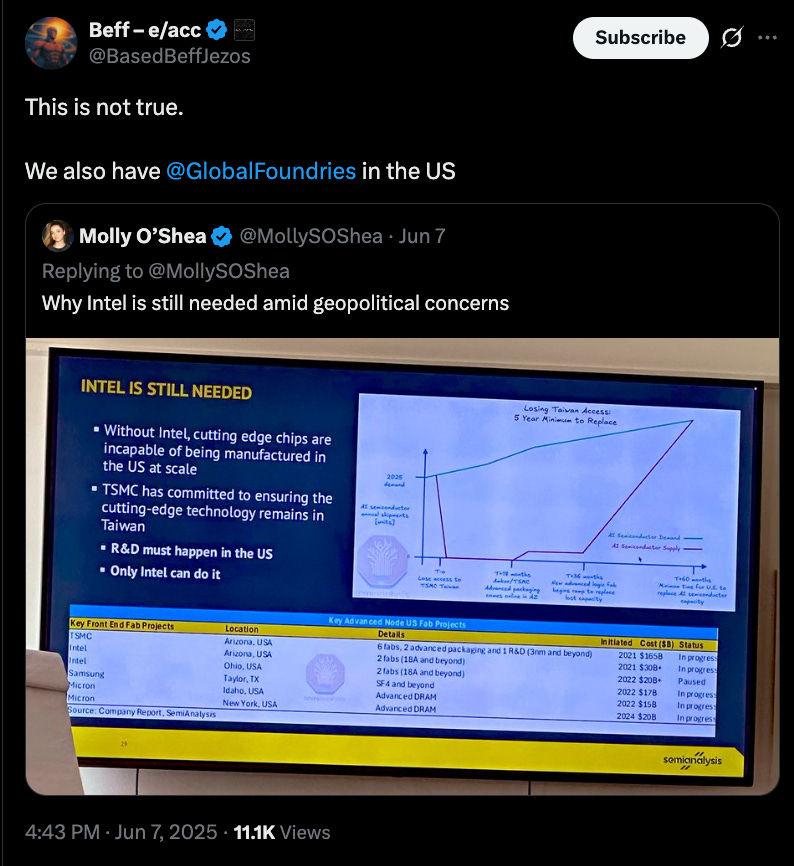
Meanwhile, foundational players like Intel and GlobalFoundries remain vital for maintaining domestic manufacturing sovereignty. Without Intel’s fabs, the U.S. cannot produce cutting-edge chips at home. And despite over $30 billion in new investments across Arizona and Ohio, these fabs alone cannot meet growing AI demand unless the power grid expands in parallel.
Of note, GlobalFoundries Inc. (Nasdaq: GFS) was left out of Dylan’s talk because of their focus away from leading-edge scaling law chips, like the ones TSMC, Samsung, & Intel offer. GFS remains a U.S.-headquartered semiconductor foundry serving critical industries such as automotive, aerospace, defense, industrial, RF, and IoT. GFS has a global manufacturing footprint across the U.S., Europe, & Asia. The company is majority-owned (~81%) by Mubadala Investment Company, the sovereign wealth fund of Abu Dhabi, via its holding arm Mamoura Diversified Global Holding (MDGH).
UAE is Already Live With A Long-Term Bet on Intelligence
In contrast, the UAE’s infrastructure is already live. With 14 million kilometers of fiber installed and 99.5% fiber-to-the-home coverage, the UAE is among the most connected countries globally. Its Stargate UAE facility sits strategically at a geographic nexus between Europe, Asia, and Africa, making it an ideal location for low-latency AI inference & global model hosting to reach half the world’s population.
“It’s no coincidence that Abu Dhabi is geographically well-positioned in that regard: it sits at the nexus of Europe-Asia-Africa internet cables, giving low-latency connectivity to billions of people.” G42
But the UAE’s ambitions go beyond scale. Through partnerships like Jais, an open-source Arabic-English large language model developed by G42’s Inception, and new national AI education initiatives (including K–12 curriculum and university AI majors), the country is aiming to build local AI fluency and capability alongside hardware. As scholar Jeffrey Ding notes, the power of general-purpose technologies like AI doesn’t come from inventors alone—it comes from wide adoption, “ordinary engineers,” and systems integration.
Finally, there is a matter of responsibility. The UAE has publicly committed to the safe, secure, and broadly beneficial use of AI, including through its participation in international safety forums and its emphasis on governance. This includes using compute not just for commercial products, but for climate modeling, drug discovery, education, and alignment testing—areas where trillion-token-scale compute could yield real breakthroughs.
In short, the UAE’s goal is not just acquiring GPUs, they recognize the significance of this opportunity and are positioning themselves as a long-term partner and leader in computational infrastructure, capable of producing and distributing intelligence at scale.
Read more on G42’s vision: From Barrels of Oil to Trillions of Tokens: The UAE’s Next Big Export, "Intelligence"
A World in Transition: What Determines AI Sovereignty Now?
AI has become increasingly central to economic strength and geopolitical power. What’s unfolding is a global reordering (or arguably, “ordering”) of AI infrastructure and industrials, where access to GPUs, sovereign fabrication, and scalable energy are just too big for just one country and will require global collaboration. The most advanced models may be built in San Francisco, but the future of where they’re trained, hosted, and deployed will depend on who controls the pipes: power, silicon, and bandwidth.
This is the defining challenge of the next decade—one that raises several trillion-dollar questions:
Can the U.S. and its allies scale compute capacity fast enough? Both at home and abroad, to outpace rivals in China, secure model sovereignty, and ensure aligned access to power?
How much can we rely on efficiency gains in chips and software to ease infrastructure pressure? NVIDIA’s Blackwell architecture and emerging inference platforms promise step-function improvements in tokens per watt, but will those advances arrive fast enough to offset physical grid limitations?
How quickly can the U.S. modernize its energy infrastructure? Especially transmission, permitting, and sustainable power generation, to meet the compute demands of AI without compromising reliability or cost?
Are we building too much too quickly—or not nearly enough? Trillions of dollars may flow into datacenter infrastructure over the coming decade, but how much of that will be wisely deployed versus stranded in unused capacity or inefficient clusters?
The balance between agility, oversupply, and national security isn’t yet clear, but it’s critically important and will likely define the winners and laggards of the AI era.
SemiAnalysis Slides





Brought to you by:
Brex—The modern finance platform, combining the world’s smartest corporate card with integrated expense management, banking, bill pay, and travel. As a Sourcery listener, you can unlock up to $500 toward Brex travel or $300 in cash back, plus exclusive perks to help you move even faster.
Kalshi—The largest prediction market and the only legal platform in the US where people can trade directly on the outcomes of future events. Beat the odds.
Fourthwall—The #1 way to sell merch online — Fourthwall is the easiest way to launch a fully branded merch store—used by big brands like MKBHD, Acquired, & even the Smithsonian. 100+ products. No upfront cost. Visit Fourthwall to start today.
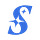





"Without coordinated national efforts to modernize the grid, accelerate permitting, and prioritize AI-relevant energy loads, the U.S. risks being outpaced by rivals with more agile energy infrastructure and sovereign industrial policy."
Two-party politics, environmentalism, and NIMBYs means national coordination on energy will basically be impossible.
But it would still be foolish to bet against America for one reason and one reason alone: Texas.
* Fourth-largest oil producer in the WORLD [1]
* The leading state for wind and large-scale solar generation despite Republican dominance [1]
* 35% increase in energy supply since 2021 [1]
* Most YIMBY mindset in the US: "We will increase capacity of our grid to ensure that every Texan has affordable, reliable power and unleash the full potential of Texas’ nuclear industry. And we will produce enough energy power on the grid to make sure that every home, every business and every location is going to have access to the power they need." - TX Gov. Abbott [1]
* 55.8 GW of generation capacity added in 2024 [2]
* 8x the land area compared to UAE
[1]: https://www.texastribune.org/2025/03/06/texas-legislature-energy-renewables-power-grid/
[2]: https://www.dallasfed.org/research/energy/indicators/2024/en2404